The Risk of Falling for Seniors: A Comprehensive Guide
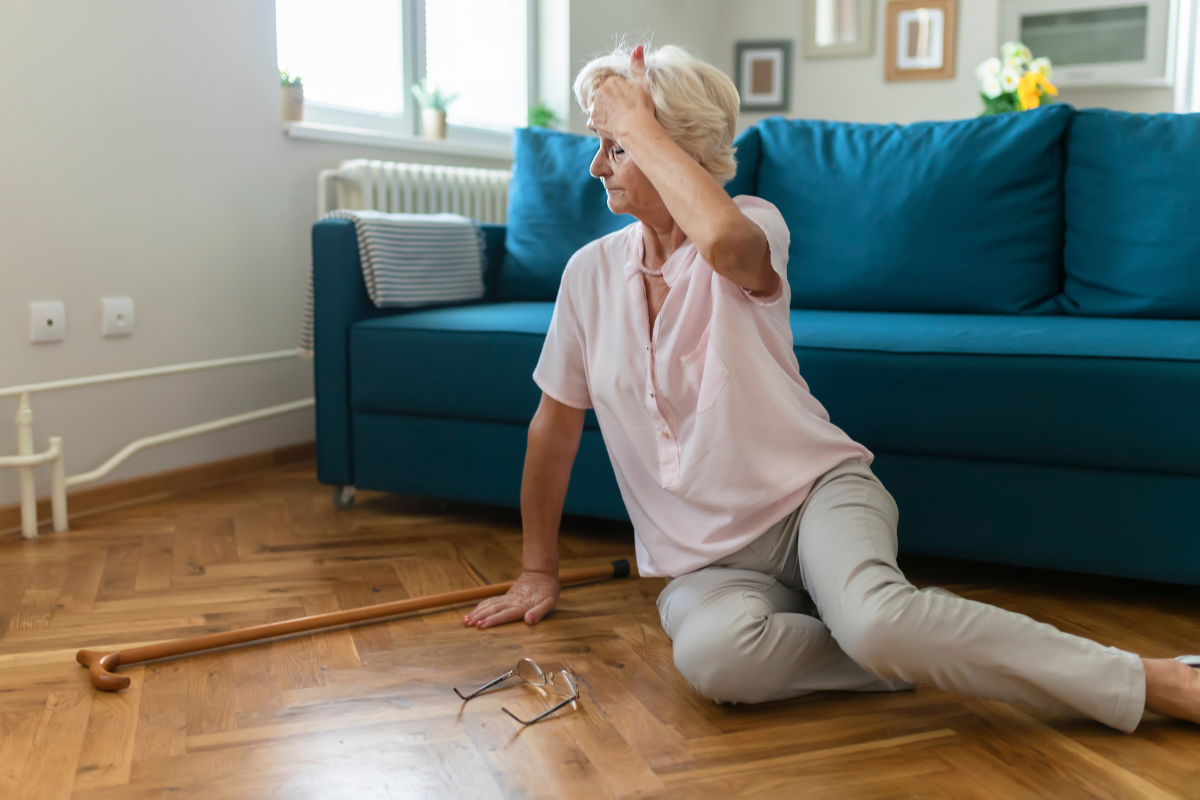 As we age, our bodies undergo various changes that can impact our overall health and well-being. One of the significant concerns for seniors is the increased risk of falls. Falls can lead to serious injuries, reduced quality of life, and even hospitalization. However, understanding the factors that contribute to fall risk can empower seniors, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to take proactive measures to prevent accidents.
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes that can impact our overall health and well-being. One of the significant concerns for seniors is the increased risk of falls. Falls can lead to serious injuries, reduced quality of life, and even hospitalization. However, understanding the factors that contribute to fall risk can empower seniors, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to take proactive measures to prevent accidents.
Physical Factors for Senior Fall Risk
Physical factors contribute significantly to the increased fall risk among seniors. These can include:
- Muscle Weakness: As we age, our muscles naturally lose strength and flexibility. Weak muscles can compromise balance and stability, making falls more likely.
- Impaired Balance and Coordination: Conditions affecting the inner ear or sensory perception can disrupt balance and coordination, increasing fall risk.
- Gait Issues: Walking patterns can change with age, making seniors more susceptible to tripping or losing their balance.
- Chronic Conditions: Health conditions like arthritis, osteoporosis, and Parkinson's disease can affect mobility and increase the risk of falls.
- Medications: Certain medications can have side effects like dizziness or drowsiness, which can significantly contribute to senior fall risk.
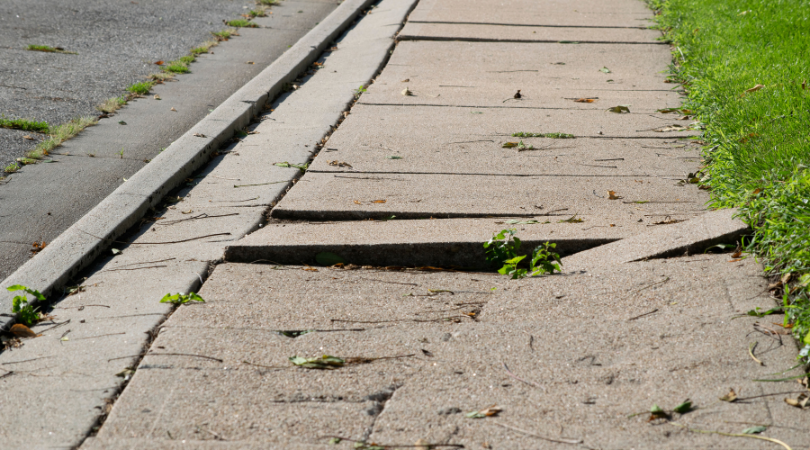

Environmental Factors for Senior Fall Risk
Environmental factors raise the risk of falling for everyone, but they create additional risk for seniors who may already be impacted by physical factors. Environmental factors can include:
- Clutter: Obstacles and clutter in living spaces can lead to tripping hazards.
- Poor Lighting: Inadequate lighting can make it difficult for seniors to see potential hazards.
- Uneven Surfaces: Uneven flooring, loose rugs, or thresholds can lead to trips and falls.
- Lack of Assistive Devices: The absence of grab bars, handrails, or mobility aids can hinder safe movement.
Psychological Factors for Senior Fall Risk
Psychological factors can amplify fall risk among seniors by reducing physical activity and affecting cognitive function. Addressing these emotional aspects is crucial for promoting safety and well-being in older adults. These factors include:
- Fear of Falling: A previous fall or the fear of falling can lead to reduced physical activity and social isolation.
- Depression: Mental health issues like depression can affect cognitive function and physical activity levels.
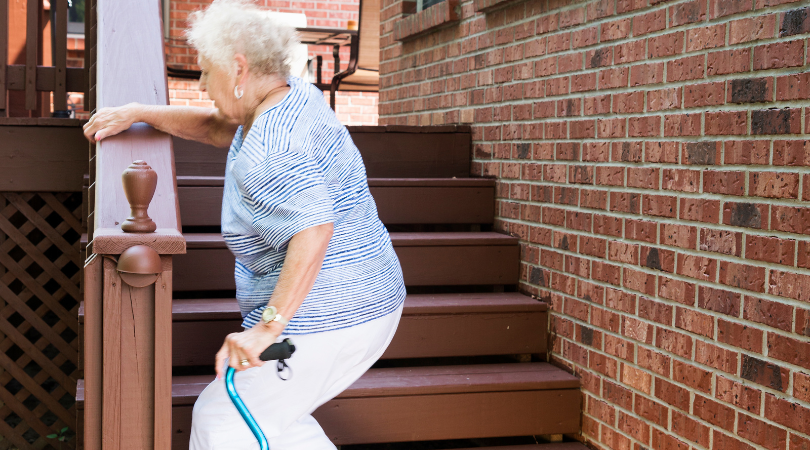

Behavioral Factors for Senior Fall Risk
Behavioral factors can heighten fall risk among seniors by compromising muscle strength, balance, and overall mobility, underlining the importance of promoting healthy habits and proper device usage to mitigate these risks. Behavioral factors include:
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles can weaken muscles, impair balance, and reduce overall fitness.
- Improper Footwear: Ill-fitting shoes or shoes without proper grip can increase fall risk.
- Improper Use of Mobility Aids: Incorrect usage of walkers, canes, or other assistive devices can lead to accidents.
Medical Factors for Senior Fall Risk
Medical factors significantly elevate fall risk among seniors by diminishing sensory perception, spatial awareness, and cognitive function, underscoring the need for regular medical check-ups and interventions to manage these conditions and enhance safety. These can include:
- Vision Problems: Poor vision, cataracts, and other eye conditions can affect depth perception and spatial awareness.
- Cognitive Impairment: Conditions like dementia can lead to confusion and a higher likelihood of falls.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Irregular heart rhythms, low blood pressure, or heart conditions can lead to fainting and falls.
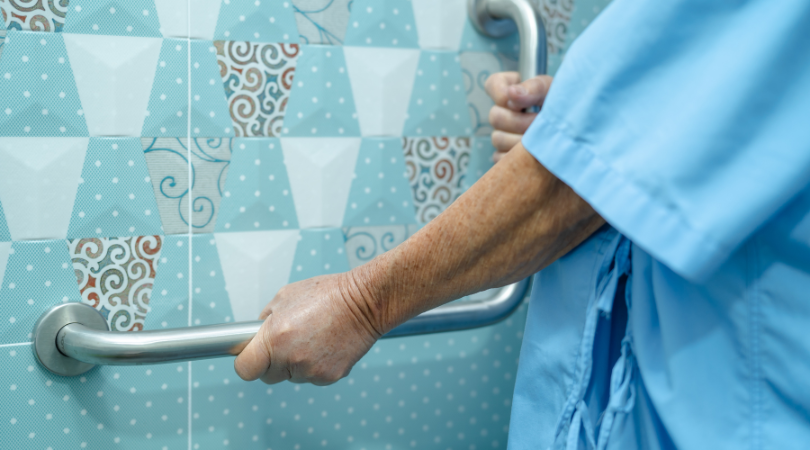

Strategies to Mitigate Fall Risks
Mitigating senior fall risk involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing regular exercise to improve strength and balance, home modifications to remove hazards, and thorough medication reviews to address side effects, ensuring a safer and more independent lifestyle for older adults. Collaboration between seniors, caregivers, and healthcare professionals is essential in implementing effective strategies for fall prevention. By taking the following steps, families can help prevent falls:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in strength, balance, and flexibility exercises can improve muscle tone and stability.
- Medication Review: Regularly reviewing medications with a healthcare provider can help identify those that may increase fall risk.
- Home Modifications: Removing hazards, improving lighting, and installing grab bars can create a safer living environment.
- Vision and Hearing Check-ups: Regular eye and hearing exams help maintain sensory function.
- Footwear: Wearing well-fitting, non-slip footwear is essential for stability.
- Nutrition: Ensure your loved one is maintaining a healthy diet and staying properly hydrated.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can identify and address health issues that contribute to fall risk.
Understanding fall risk factors among seniors is essential for maintaining their safety and well-being. By addressing these factors through lifestyle modifications, environmental changes, and regular healthcare, seniors can maintain their independence and enjoy a higher quality of life in their golden years.
Crossroads Hospice & Palliative Care provides support to patients experiencing serious and terminal illness. To learn more about our services, please call 1-888-564-3405.
If you found this information helpful, please share it with your network and community.
Copyright © 2023 Crossroads Hospice. All rights reserved.